
Here is how you can enable or disable applications and services that automatically start at Startup in Windows
Windows, being a general-purpose operating system, is made up a ton of micro-services, drivers, and different first-party, as well as third-party softwares working together in order to provide you with the ideal experience. In the early days of the Windows operating system, Microsoft bundled in only a few software drivers in order to keep the disk space taken up by Windows small since memory wasn’t as cheap in those days as it is today. These worked with most commonly-used devices but not all of them, so most devices came with their own CDs with the driver-installation wizards on them.
Today, with the drastic increase in memory sizes, Windows has built in most drivers in the operating system itself. However, not all of these drivers and services are being used to do. Still, Windows starts some of these by default at Windows startup. Moreover, there are a lot of services that Windows startups by default that you don’t really use in your daily lives, but only slow down your PC a little bit.
Fortunately, Windows allows you a significant amount of control over how your PC runs. You can very easily change and control what services and applications you want Windows to start when it starts up and which ones to disable. There are several ways you can achieve this: here, we will list down all the ways you can enable or disable applications and services from starting at startup in Windows,
Note: The method differs a little bit, depending on which version of Windows you are on. So, we have split the guide up in different portions, for Windows 7 and earlier users, and for users of Windows 8, 8.1 and 10.
Adding or Deleting Apps through Startup Folder
WINDOWS 8, 8.1, and 10
- Press START + S to open search in Windows and search for the app that you want to enable at startup. Right-click on it and click on Open file location. (If you don’t see this option, you probably won’t be able to make this app run at startup time)

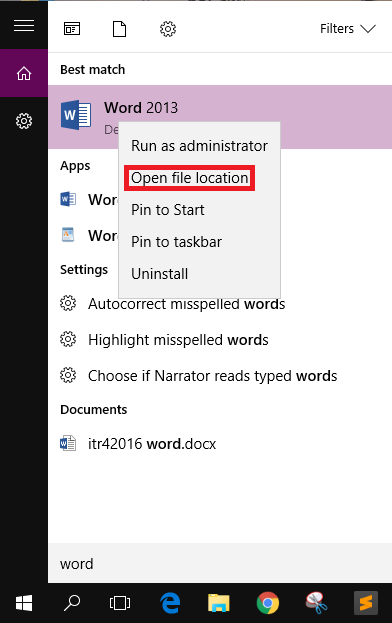
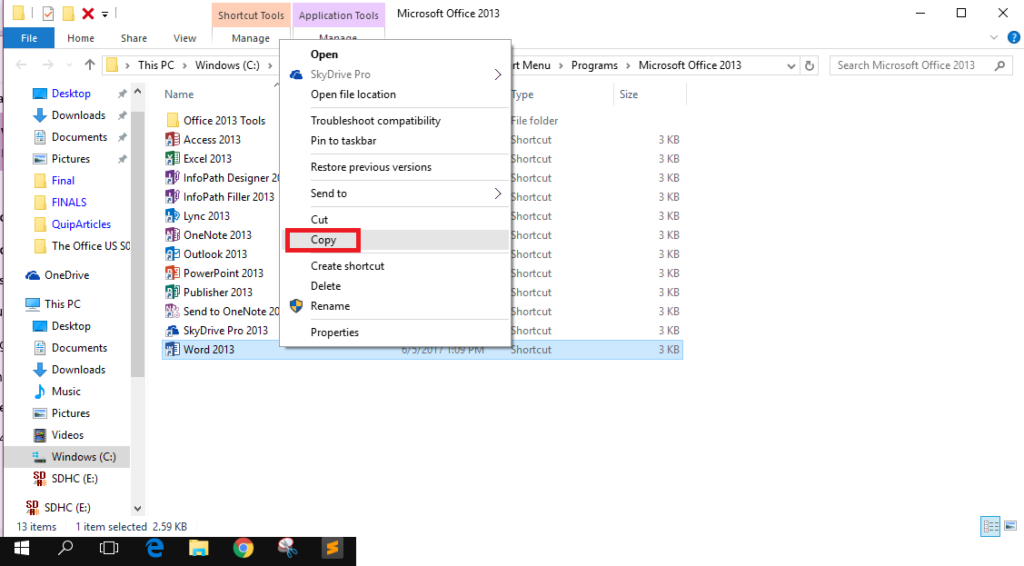
- It will open the folder which stores the shortcut to the file’s executable, which is responsible for launching the program. Copy the shortcut by right-clicking on it and selecting Copy.
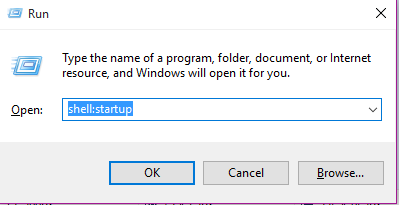
- Press START + R to open the Run dialog box and type the following command, and click on OK.
shell:startup
- It will open the Startup folder. Paste the file you copied earlier by right-clicking inside the folder and clicking on Paste.

WINDOWS 7
- Copy the shortcut of the program you want to run at startup.
- Press the START button, then click on All Programs and then click on Startup.
- It will open the Startup folder. Paste the file you copied earlier by right-clicking inside the folder and clicking on Paste.

That’s it. Windows will now launch this program automatically at Startup time. You can also delete programs from here that you don’t want Windows to start. Since they are just shortcuts, deleting programs from here will only disallow Windows from launching those at startup, not physically delete the programs from your computer. Moreover, if a shortcut here is pointing to the wrong program, you can also correct it by right-clicking on the icon, selecting Properties, going to the Shortcut tab and pasting the correct path to the filename of the correct program in the Target: field.
Not in the Startup Folder? Here is how you can Enable or Disable Them
WINDOWS 8, 8.1, AND 10
- Open the Windows Settings app by pressing on START + I.
- Click on Apps and then select Startup from the left pane.
- Select the app you want to run at startup and switch it to On.
If the above option is not available in the Settings app, follow the steps given below,
- Open the Task Manager. You can do it by pressing START + X and clicking on Task Manager in the box that appears.

- Go to the Startup tab. It will show you a list of all the applications that are registered with Windows to be started at startup time.

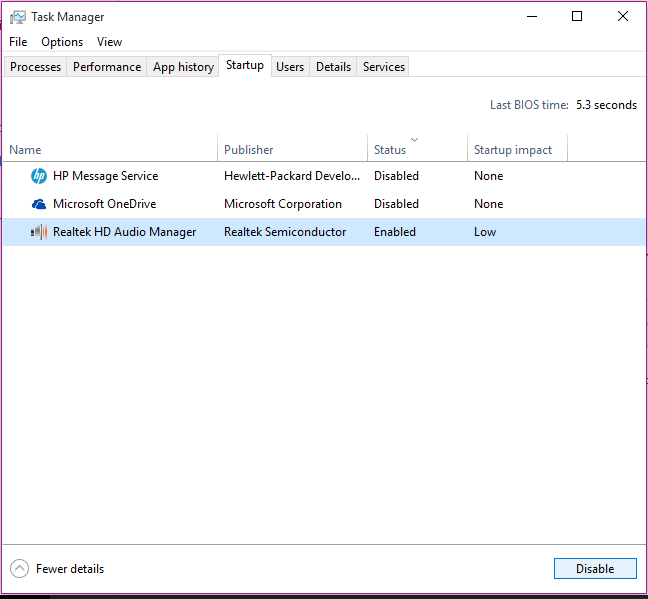
It will also show the Status (if the app is currently Disabled or Enabled) and the impact it has on startup (in terms of how much time and performance impact it has). You can click on any app and click on Enable (if it is disabled) or Disable (if it is enabled). If you see any services that you don’t recognize, you should search them on the web before disabling them because they may be essential to the workings of your PC. For example, the Realtek HD Audio manager, listed on the startup in the screenshot below, is responsible for audio processing.
WINDOWS 7
- Press on START + R to open the Run dialog box. Type msconfig and then click on OK.
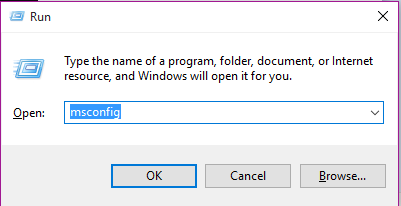
- Go to the Startup tab, as shown in the attached screenshot.
- Simply check the items you want to start at startup and uncheck the ones you don’t.
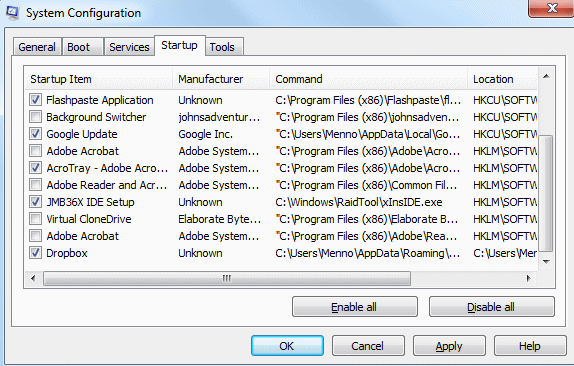
- Once you’re done, click on OK.
- Windows will ask you to Restart your computer in order to apply your changes. Click on Restart.
If there are still some programs that are being launched by Windows at startup time, you might need to make a change in the Windows Registry using the Windows Registry Editor. However, do go through our guide for editing the Windows Registry before proceeding with the next step.
Enable or Disable Programs at Startup through Windows Registry
- Press on START + R to open the Run dialog box. Type regedit and then click on OK.

- We recommend making a backup of the Windows Registry before you proceed using our guide since editing the Windows Registry is a risky process and having a backup means you can revert back any time you want.
- Expand the HKEY LOCAL MACHINE option by clicking on the little ‘+’ sign next to it, then expand SOFTWARE > Microsoft > Windows > CurrentVersion.
- Click on the Run folder to open it and on the right side of the screen, you will see a list of all the programs that are set to run on startup.
- Just click on any program that you do not want to run at startup time, right-click on it and click on Delete.

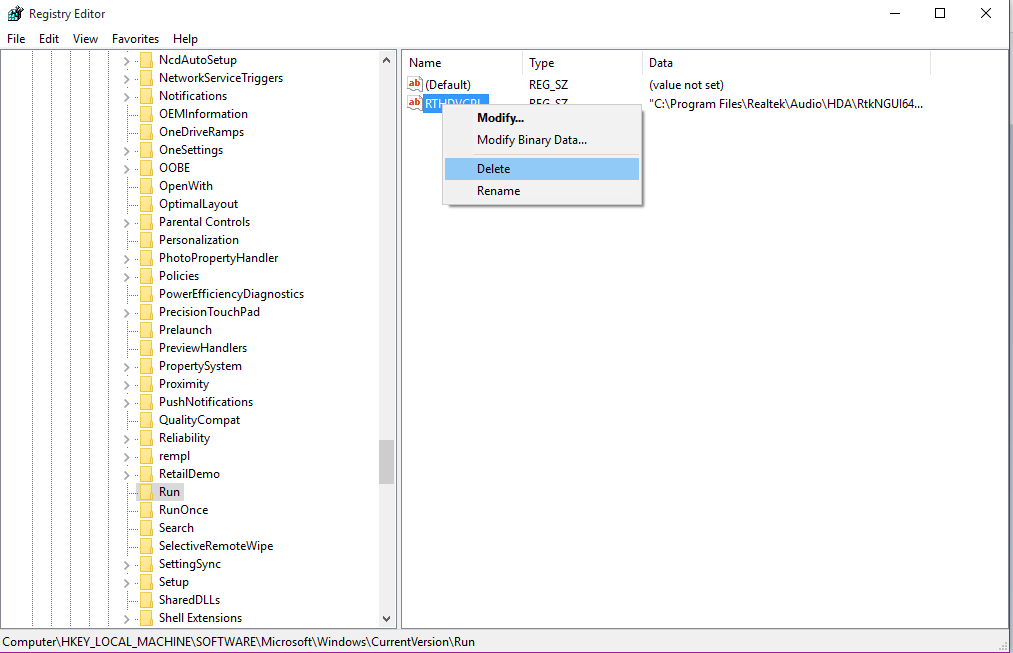
That’s it. Just close Windows Registry Editor and you’re good to go. You can restart to see if the changes you made worked.

